In the ever-evolving world of cannabis, a myriad of compounds are gaining attention for their unique effects and potential benefits. among them, THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) and THC D9 (Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol) stand at the forefront of scientific and recreational discussions alike. while they share a common lineage, their differences warrant a closer examination, especially as more individuals seek too understand how these cannabinoids can fit into their wellness journeys. This article delves into the distinctive characteristics of THCA and THC D9, shedding light on their chemical structures, effects, and applications, ultimately aiming to clarify the distinctions that may influence your choices in the vibrant cannabis landscape. Join us as we uncover the key differences between these two fascinating compounds, providing a clearer understanding of their roles within the broader context of cannabis and its myriad benefits.
Exploring the Chemical Structures of THCA and THC D9
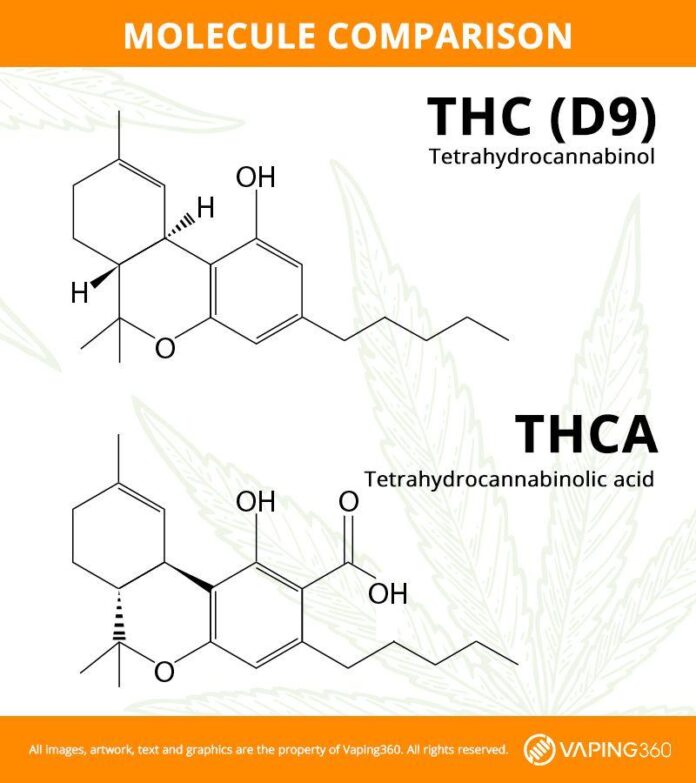
The chemical structures of THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and THC D9 (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) are fundamental to understanding their differing effects and roles in the cannabis plant. Both compounds share the same molecular formula, C21H30O2, but their structural makeup leads to notable variations in their psychoactive properties.THCA is the carboxylic acid form of THC, which means it has a carboxyl group (-COOH) that is not present in THC D9.This small but crucial difference prevents THCA from producing the euphoric effects typically associated with its decarboxylated counterpart.
When THCA is exposed to heat through processes such as smoking or cooking, it undergoes decarboxylation, releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) and transforming into THC D9. This conversion highlights the importance of temperature in determining the active components of cannabis. Below are a few key structural differences that influence their respective behaviors:
- THCA: Contains a carboxyl group, rendering it non-psychoactive.
- THC D9: Lacks the carboxyl group, leading to psychoactive effects.
- Activation Mechanism: THCA requires heat to convert into THC D9.
The distinct chemical makeup of these cannabinoids not only dictates their effects on the human body but also influences their therapeutic potential. While THC D9 is widely recognized for its psychoactive properties, THCA is garnering attention for its potential anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-nausea benefits without the high. Understanding these structural differences offers valuable insights into optimizing cannabis use for various purposes.
Understanding the Effects: How THCA and THC D9 Interact with the Body
When examining the interactions of THCA and THC D9 with the human body, it’s essential to recognize their distinct characteristics and effects. THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC. It primarily interacts with the body through the endocannabinoid system, influencing receptors without producing a high.Users may experience benefits such as:
- Anti-inflammatory properties, helping reduce inflammation and pain.
- Neuroprotective effects, perhaps aiding in conditions like neurodegeneration.
- Appetite stimulation, supporting those who struggle with eating due to medical conditions.
In contrast, THC D9 or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound found in cannabis. Upon consumption, it binds more intensely with CB1 receptors in the brain, leading to significant alterations in perception, mood, and cognition. The effects frequently enough include:
- Euphoria and relaxation, creating a sense of well-being.
- Anxiety relief, even though some users may experience heightened anxiety.
- Pain relief, effectively addressing chronic pain in many users.
The interaction between these two compounds can also lead to a more nuanced experience when used together, as THCA may mitigate some of the psychoactive effects of THC D9. This synergy highlights why many consumers and cultivators are increasingly interested in the ratios and combinations of cannabinoids. To provide a clearer view,consider the following table summarizing key differences:
| Feature | THCA | THC D9 |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactivity | Non-psychoactive | Psychoactive |
| Medical Benefits | Anti-inflammatory,neuroprotective | Pain relief,mood enhancement |
| Binding Affinity | CB2 receptors | CB1 receptors |
medical Benefits and Therapeutic Uses of THCA versus THC D9
When it comes to therapeutic applications, both THCA and THC D9 demonstrate distinct advantages, making them appealing for a variety of medical conditions. THCA, the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, has gained attention for its potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. This cannabinoid is believed to interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system without producing the euphoric effects associated with THC D9. As a result, many patients, especially those seeking relief from chronic pain or inflammation, find THCA beneficial in managing their symptoms without the high.
On the othre hand, THC D9 is renowned for its psychoactive effects and is frequently enough utilized in medical settings for its ability to alleviate nausea, stimulate appetite, and provide pain relief. It is particularly effective for patients undergoing chemotherapy or those suffering from severe appetite loss due to various conditions. The immediate psychoactive effects allow for rapid symptom management,which can be crucial in acute medical situations. However, for some patients, these effects may be undesirable, which is where THCA shines as a potent option.
To understand the comparative benefits of these cannabinoids, consider the following table highlighting key differences in their therapeutic uses:
| Property | THCA | THC D9 |
|---|---|---|
| Psychotropic Effects | no | Yes |
| Common Uses |
|
|
| Preferred Patient Type | Those avoiding intoxication | Those seeking quick relief from acute symptoms |
Legal Considerations and Regulatory Differences in Various Regions
The legal landscape surrounding THCA and THC D9 is intricate and varies significantly across different regions. In some areas, THCA is viewed as a non-psychoactive substance, allowing its use and possession under lenient regulations. Conversely, THC D9, with its psychoactive properties, often faces stringent controls. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for consumers, dispensaries, and manufacturers aiming to navigate the complex regulatory environment.
Regulatory frameworks can differ not only between countries but also within states or provinces. As an example, the following factors influence the regulation of cannabis products:
- State laws: Each state has its own stance on medicinal and recreational cannabis.
- Federal legislation: In certain countries, cannabis-related laws at the national level can override local statutes.
- Medical usage allowances: Some regions permit the use of THCA for medical purposes, while others restrict all forms of cannabis.
To illustrate the variability in regulations,the table below highlights how different regions perceive THCA and THC D9:
| Region | THCA Regulation | THC D9 Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| California | Permissive | Legal (with restrictions) |
| New York | Legal (medical only) | Legal (recreational) |
| Germany | Legal (medical only) | Strictly regulated |
| Japan | illegal | Illegal |
Consumption Methods: Choosing the Right Form for Your Needs
When considering the best consumption methods for your needs, understanding the distinct characteristics of THCA and THC D9 is essential. Each form has its unique effects and benefits, which can make a significant difference in your overall experience. If you’re seeking therapeutic effects without the psychoactive high, THCA is the preferred choice as it is indeed the non-intoxicating precursor to THC.On the other hand, THC D9 delivers the euphoric effects typically associated with cannabis, making it suitable for those looking for a more potent experience.
When selecting a consumption method, consider the following options available for both compounds:
- Inhalation: Vaping or smoking cannabis flower delivers immediate effects, ideal for users seeking quick relief.
- Edibles: Consuming cannabis-infused foods provides a longer-lasting effect, but the onset time is slower.
- Tinctures: These allow precise dosing and quick absorption, suitable for both THCA and THC D9 users.
- Topicals: Perfect for localized relief, particularly beneficial for users focused on specific areas of discomfort.
To help guide your decision, here’s a brief comparison of the two compounds in relation to common consumption methods:
| Consumption Method | THCA | THC D9 |
|---|---|---|
| Inhalation | No high, potential for anti-inflammatory effects | Immediate high, mood enhancement |
| Edibles | Therapeutic benefits, longer onset | Strong psychoactive experience |
| Tinctures | Versatile and fast-acting | Control over dosage and effects |
| Topicals | Localized relief without psychoactivity | Limited effect due to low absorption |
Guidelines for Responsible Use and Dosage Recommendations
When experimenting with either THCA or THC D9, it’s crucial to consider individual tolerance levels and desired effects.Each compound interacts differently with the body,depending on personal biochemistry. Start with a low dose to assess your reaction before gradually increasing. this cautious approach helps prevent any unwanted side effects and ensures a more pleasant experience.
For those new to cannabis or unfamiliar with these cannabinoids, it’s wise to adhere to the following dosage guidelines:
- Begin with low doses: Start with 5-10 mg of THCA or THC D9.
- Observe effects: Wait for at least 1-2 hours to gauge your experience before taking more.
- Increase gradually: If needed, increment up to 5 mg at a time until desired effects are achieved.
Understanding the duration of effects can also aid in responsible use. Here’s a simple comparison of how long you might expect effects to last from both compounds:
| Cannabinoid | Onset Time | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| THCA | 1-2 hours (ingested) | 2-4 hours |
| THC D9 | 30 minutes - 1 hour (smoked) | 3-6 hours |
Final thoughts
In the intricate world of cannabis, the distinctions between THCA and THC D9 shed light on the multifaceted nature of this remarkable plant. While both compounds are integral to the broader cannabis narrative, their unique characteristics and effects pave the way for diverse experiences and therapeutic potentials. Understanding these differences not only equips consumers and patients with vital knowledge but also opens the door to deeper exploration and appreciation of cannabis and its myriad benefits. As the landscape of cannabis continues to evolve, the conversation surrounding cannabinoids remains as vibrant as ever, inviting both curiosity and discovery. Whether you’re a seasoned connoisseur or a curious newcomer, knowing the nuances of THCA and THC D9 will enhance your journey through the world of cannabis. With each puff and pinch,there lies an possibility to uncover more about what these compounds can offer,ensuring that every experience is informed and enriching.