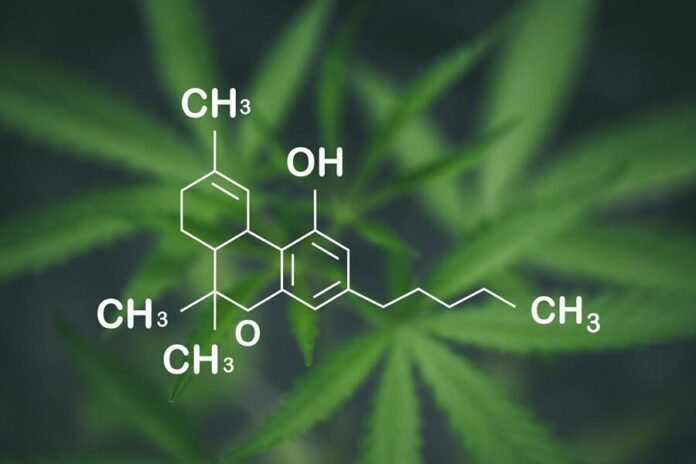
In the ever-evolving landscape of cannabis, where terms like THC and CBD have become part of everyday vocabulary, there lies a lesser-known compound that deserves the spotlight: tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, or THCA. Often overshadowed by its more famous cousin, Delta-9 THC, THCA is gaining attention for its unique properties and potential benefits. Yet, as curiosity grows, so does the confusion-why does this compound matter, and how does it fit into the larger cannabinoid picture? In this exploration of THCA, we’ll delve into what differentiates it from Delta-9 THC, its role in the plant’s chemistry, and the implications for users and researchers alike. join us as we decode the intricacies of THCA, unraveling the myths and revealing the truths behind this enigmatic compound, to understand whether it truly is the Delta-9 you thought you knew.
Understanding THCA: The Basics Beyond Delta 9
As cannabis gains more mainstream acceptance, the conversation around cannabinoids is evolving. One lesser-known compound that has sparked interest is tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA). While most are familiar with Delta-9 THC,the psychoactive component of cannabis,THCA presents a different story altogether. Unlike Delta-9, THCA is non-psychoactive in its raw form, which means it doesn’t produce the high typically associated with cannabis consumption. This distinction makes THCA a fascinating subject for both researchers and enthusiasts alike.
THCA is primarily found in the raw, unheated cannabis plant. When cannabis is heated through processes like smoking or vaporizing, THCA undergoes decarboxylation, converting it into Delta-9 THC. This transformation is notable because it highlights the potential therapeutic benefits of THCA in its untouched state. Many advocates suggest that consuming THCA may retain the anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and analgesic qualities without the intoxicating effects of Delta-9.Some potential benefits of THCA include:
- anti-inflammatory properties: THCA may help reduce inflammation, making it attractive for conditions like arthritis.
- Neuroprotective effects: Early research suggests THCA could play a role in protecting the nervous system.
- Appetite stimulation: Unlike Delta-9, which can increase appetite considerably, THCA may aid in healthy appetite without overwhelming cravings.
To put things in outlook, let’s take a look at a comparison between THCA and Delta-9 THC:
| Feature | THCA | Delta-9 THC |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactivity | Non-psychoactive | Psychoactive |
| Therapeutic Potential | Anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective | Analgesic effects, euphoria |
| Source | Raw cannabis plant | Heated cannabis |
This comparison serves to highlight the unique attributes of THCA, particularly for those seeking medicinal benefits without the mental cloudiness that might accompany Delta-9 THC. As cannabis research continues to grow, understanding these compounds better may pave the way for more targeted treatments and a deeper gratitude for the plant’s diverse offerings.
The Science of Cannabinoids: How THCA Differs from Delta 9
The fascinating world of cannabinoids is often dominated by the well-known Delta 9 tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta 9 THC), but lurking in the shadows is its acidic precursor, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA).While both compounds are derived from the Cannabis sativa plant,their properties and effects are markedly different,showcasing the complexity of the cannabis plant’s chemistry.
Delta 9 THC is famous for its psychoactive properties; it binds effectively to the body’s endocannabinoid receptors,particularly CB1 receptors in the brain,inducing the typical ‘high’ associated with cannabis use. In contrast, THCA is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that exists in raw cannabis. It requires a process called decarboxylation, typically achieved by heating (smoking, vaping, or cooking), to convert into Delta 9 THC. Until that process occurs, THCA does not produce the euphoric effects many associate with cannabis.
| property | delta 9 THC | THCA |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactivity | Yes | No |
| Source | Heated cannabis | Raw cannabis |
| Health Benefits | Appetite stimulant,pain relief | Anti-inflammatory,neuroprotective |
The health benefits associated with these cannabinoids also differ significantly. Delta 9 THC is frequently used for its therapeutic effects, such as relief from chronic pain, anxiety, and nausea. however, it also may cause side effects like paranoia or anxiety in some users, particularly at higher doses. Conversely,THCA has garnered attention for its potential therapeutic properties without the intoxicating effects.Users and researchers alike have noted its possible role in reducing inflammation and supporting neurological health, making it an intriguing subject of study.
Understanding the differences between these two cannabinoids is essential for consumers and patients alike, highlighting the importance of the specific formulation of cannabis products. As the cannabis industry continues to evolve, distinguishing between THCA and Delta 9 THC will aid in guiding users toward the desired effects and benefits of each, paving the way for informed choices in their cannabis consumption journey.
Potential Benefits of THCA: What Research Reveals
the potential benefits of THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid), though still under investigation, have shown promising insights in recent studies. Unlike its more famed counterpart, Delta-9 THC, THCA does not produce psychoactive effects, making it a point of interest for those seeking therapeutic support without the high. Research suggests that THCA may possess a range of medicinal properties, perhaps aiding in the management of various conditions.
Some of the touted benefits of THCA include:
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Preliminary studies indicate that THCA may play a role in reducing inflammation, which could be beneficial for those suffering from conditions like arthritis or Crohn’s disease.
- Neuroprotective effects: THCA has shown promise in preclinical trials for its ability to protect brain cells, suggesting potential therapeutic avenues for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Anti-emetic effects: Research hints at THCA’s potential to help alleviate nausea and vomiting,which could be particularly useful for patients undergoing chemotherapy or dealing with other nausea-inducing treatments.
- Appetite stimulation: while traditionally linked to its psychoactive cousin, THCA may also contribute to increased appetite without the associated high, offering a potential aid for those struggling with appetite loss.
Moreover,in a recent study conducted by a team at the University of Northern Colorado,researchers evaluated the various cannabinoid profiles available in raw cannabis,highlighting the significance of THCA in its unheated state. The findings reinforce the idea that the raw form of the plant may hold benefits worth considering, challenging the notion that only activated cannabinoids are worthy of attention.
| Condition | Potential THCA Benefit |
|---|---|
| Arthritis | Reduces inflammation |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Neuroprotective support |
| Chemotherapy | Alleviates nausea |
| Appetite Loss | Stimulates appetite |
Consumption Methods: Exploring THCA Products and Their Effects
As interest in the cannabis plant evolves,consumers are increasingly exploring the spectrum of cannabinoids that go beyond the well-known delta-9 THC. one such compound is THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid), the non-psychoactive precursor to delta-9 THC. Understanding how to consume THCA products can dramatically influence therapeutic outcomes and user experiences.
There are various forms of THCA products available on the market, each offering unique consumption experiences. Some popular options include:
- Raw Flower: fresh cannabis flower that has not been decarboxylated retains its THCA content, enabling users to utilize it in salads, smoothies, or juices for a natural boost.
- Tinctures: Alcohol or oil-based tinctures infused with THCA provide an easy-to-dose and fast-acting method of consumption, suitable for both beginners and experienced users.
- Vape Products: Vaporizing THCA extracts can enhance the flavor profile and aroma while providing a more efficient way to consume cannabinoids without combustion.
- edibles: Though less common due to the need for decarboxylation to activate delta-9 THC, specialized THCA-infused edibles offer a unique way to experience the benefits of the cannabinoid without the high.
When considering the effects of THCA,many users report distinct experiences compared to delta-9 THC. Notable benefits often attributed to THCA include:
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: THCA may aid in reducing inflammation and pain.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Emerging research indicates THCA has potential neuroprotective qualities that could benefit those with neurological disorders.
- Appetite Stimulation: Some users find that THCA products help stimulate appetite without the psychoactive effects associated with delta-9 THC.
Considering these variances, individuals curious about integrating THCA into their wellness routines should experiment with different consumption methods to discover what works best for them without the psychoactive influence of delta-9 THC.Each method provides an chance to experience the benefits of cannabis while sidestepping the high associated with more traditional forms of consumption.
Legal Landscape: Navigating THCA Regulations and Implications
The burgeoning interest in THCA has brought with it a complex interplay of local, state, and federal regulations. Unlike its more notorious cousin, Delta-9-THC, THCA is often perceived as a more benign compound, particularly in jurisdictions where cannabis is not fully legalized. However, the legal landscape surrounding THCA is anything but straightforward. Navigators in this area must familiarize themselves with a patchwork of laws that can change not only between states but also within them.
Key considerations regarding THCA regulations include:
- Definition and Classification: How THCA is classified under cannabis laws varies significantly. Some states consider it a controlled substance, while others do not.
- Legislation Status: Various jurisdictions have implemented laws either embracing or banning THCA and related compounds.
- Compliance Obligations: Businesses dealing with THCA must ensure they meet compliance obligations, which may involve strict labeling and testing requirements.
A notable point of contention lies in the interpretation of the Farm Bill. Passed in 2018,it legally defined hemp as cannabis marijuana containing less than 0.3% THC on a dry weight basis. Advocates argue that THCA derived from hemp follows suit, yet regulators are divided on this interpretation. It’s crucial for stakeholders to continually monitor the evolving legal interpretations to navigate the landscape effectively.
As the market evolves, so too do the legal implications:
| Aspect | Implication |
|---|---|
| interstate Commerce | Varied legality complicates shipping across state lines. |
| Product Formulations | Thorough analysis of ingredients for legal compliance is mandatory. |
| Medical Use | Medical applications may differ widely in acceptance and legality. |
As more consumers and businesses engage with THCA, understanding its legal nuances becomes paramount. Engaging legal counsel experienced in cannabis law can help clarify these complex waters, ensuring that stakeholders remain compliant and informed.
Future Trends: THCA in the Evolving World of Cannabis Research
The landscape of cannabis research is rapidly evolving, and with it, our understanding of compounds like THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid). Unlike its more infamous counterpart, THC, THCA operates in a subtler realm, presenting a plethora of potential therapeutic benefits that are just beginning to garner attention. As researchers dive deeper, we are witnessing a shift in focus towards the acidic cannabinoids, offering a fresh perspective on the plant’s full spectrum of effects.
Current studies suggest that THCA may possess neuroprotective properties, anti-inflammatory effects, and even anti-emetic benefits.Unlike THC, THCA does not produce psychoactive effects, making it a highly appealing option for patients seeking relief without the high. This characteristic positions THCA as a versatile compound in the medicinal cannabis domain, promoting the idea that the cannabis plant holds much more than just recreational potential.
Future research is likely to explore the following trends:
- Synergistic Potential: Investigating how THCA interacts with other cannabinoids and terpenes to enhance therapeutic outcomes.
- Forms of Consumption: Expanding the range of products that can be made with raw cannabis to preserve THCA’s potential benefits.
- Genetic and Environmental Factors: Understanding how different strains and growing conditions can affect THCA production.
As we progress, the intersection of technology and research will play a crucial role in amplifying our knowledge of THCA. Innovative extraction methods and analytical techniques will enable the botanical community to assess the full range of THCA’s properties and applications. This evolution could redefine how we approach cannabis-based therapies, challenging long-held assumptions and opening the door to a future where THCA stands alongside THC in the spotlight of cannabis research.
The Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of cannabis, THCA presents a curious puzzle that beckons further exploration. As we’ve unraveled the complexities of this intriguing cannabinoid,it becomes evident that THCA is much more than a mere precursor to the well-known Delta-9 THC. It casts its own unique shadow in the world of cannabinoids, offering a distinct profile that challenges conventional understanding.
As we bring our exploration to a close, it’s clear that while the allure of Delta-9 THC continues to dominate conversations, THCA deserves its moment in the spotlight. Its potential therapeutic benefits and non-psychoactive nature open new avenues for research and consumer interest alike.
With ongoing studies and a growing body of knowledge,the cannabis community is poised to redefine not only the way we perceive THCA but also how we interact with the plant as a whole. So as we stand at the intersection of science and experience, remember that every cannabinoid tells a story-one that invites us to listen, learn, and ultimately, broaden our understanding of what cannabis can offer. The journey doesn’t end here.It has only just begun.