in the ever-evolving world of cannabis, understanding the nuances between its myriad compounds can be as intricate as the plant itself. Among the most talked-about players in this field are THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), two cannabinoids that hold the key to unlocking unique experiences and effects for users.While they share a common precursor, their characteristics and impacts diverge substantially, opening the door to a deeper exploration of potency and purpose. This article delves into the essential differences between THCA and THC, shedding light on their respective roles in wellness, recreation, and the science of cannabis consumption. Join us as we navigate through the complexities of these compounds, unraveling what they meen for your cannabis experience and how they interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system. Whether you are a seasoned enthusiast or a curious newcomer, understanding these cannabinoids is vital for making informed choices tailored to your needs.
Understanding the basics of THCA and THC
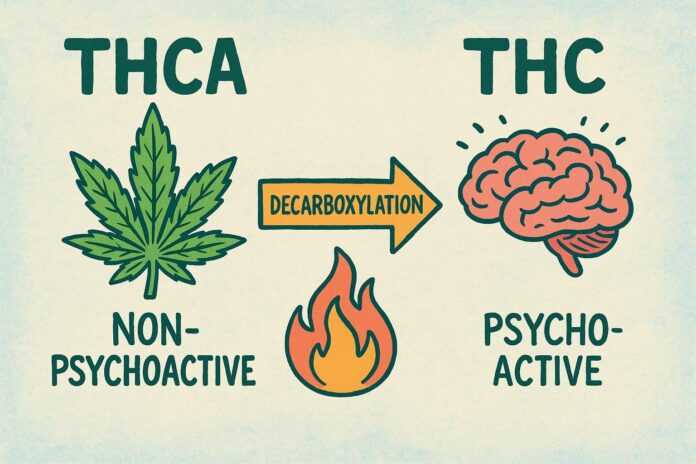
In the realm of cannabis, two compounds often take center stage: THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) and THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol). Both are pivotal in understanding the plant’s potential, yet they present distinctly different characteristics. THCA is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, meaning that it does not produce the euphoric effects commonly associated with cannabis when consumed in its raw form. This conversion occurs with heat, a process known as decarboxylation, which transforms THCA into active THC.
When discussing potency, it’s critically important to highlight that THCA is generally viewed as the “raw” version, offering therapeutic benefits without the psychoactive effects.This makes it a compelling option for individuals seeking relief from conditions such as inflammation or pain without the high. On the other hand, THC is celebrated for its ability to produce psychoactive effects, which can induce feelings of euphoria, relaxation, or even heightened sensory perception.
To further illustrate their differences, consider the following table:
| Property | THCA | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactive | No | Yes |
| Medicinal Benefits | Anti-inflammatory, Neuroprotective | Pain Relief, Appetite stimulation, Sleep Aid |
| Activation Method | None (raw form) | Heat (decarboxylation required) |
Understanding these differences plays a crucial role in selecting products based on desired outcomes. For example, individuals who prefer to avoid high concentrations of THC might gravitate towards THCA-rich strains or products, such as raw cannabis juices or tinctures. In contrast, those looking for recreational or certain therapeutic effects may opt for high-THC products. By recognizing the unique profiles of THCA and THC,consumers can make informed choices that align with their health objectives and lifestyle preferences.
Comparative Analysis of Potency Levels
The potency levels of THCA and THC can be likened to two sides of the same coin; both exhibit unique characteristics that make them valuable in different contexts. THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, which means it does not produce the euphoric high typically associated with cannabis. This fundamental difference plays a crucial role in the effects experienced by consumers and underscores the importance of understanding the nuances between the two.
When comparing the potency of these two cannabinoids, it is important to consider the following aspects:
- Activation Process: THCA requires decarboxylation, meaning it must be heated (e.g., through smoking or cooking) to convert into its psychoactive form, THC.
- Effect Profile: While THC is celebrated for its intoxicating effects,THCA is gaining attention for its potential therapeutic benefits without the high. Users frequently enough report feelings of clarity and focus when consuming THCA-rich products.
- Medical Applications: THCA is associated with neuroprotective properties and may alleviate inflammation, whereas THC is frequently utilized for pain management, appetite stimulation, and reducing nausea.
The potency differences can also be visualized through a simple comparison table outlining the characteristics of each cannabinoid:
| Cannabinoid | Potency Level | Psychoactive Effects | Potential Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| THCA | Non-psychoactive | No | anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective |
| THC | Psychoactive | Yes | Pain relief, appetite stimulation, nausea reduction |
Ultimately, the choice between THCA and THC hinges on individual preferences and the desired effects. The burgeoning interest in THCA suggests a shift in how consumers approach cannabis, emphasizing wellness over customary recreational use. Recognizing the potency variations is key to navigating the diverse landscape of cannabis products effectively.
Decoding the Effects: How THCA and THC Differ
In the world of cannabis, understanding the nuanced differences between THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is essential for consumers seeking specific effects. While they both originate from the same plant, their characteristics and impacts on the human body can diverge significantly. THCA is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, existing primarily in raw cannabis. When heated or decarboxylated, it transforms into THC, the compound well-known for its euphoric effects.
The effects of THCA are subtle yet intriguing. Users often report experiencing benefits such as:
- Anti-inflammatory properties: THCA may aid in reducing inflammation without the psychoactive effects.
- Neuroprotective benefits: Some studies suggest THCA could play a role in protecting nerve cells.
- Appetite stimulation: It may promote a sense of hunger without the high associated with THC.
Conversely, THC is famed for its psychoactive properties that often lead to feelings of euphoria or relaxation. When consuming products high in THC, users might encounter a wide range of experiences, including:
- Heightened sensory perception: Colors may appear more vibrant, enhancing visual and auditory experiences.
- altered time perception: Many report that time feels like it slows down while under the influence.
- Relaxation and euphoria: THC is frequently enough sought out for its calming effects on mood and stress.
The table below summarizes the key differences between THCA and THC in terms of their chemical structure, effects, and primary uses:
| Property | THCA | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Non-psychoactive, acid form | Psychoactive, activated form |
| Effects | Anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective | Euphoria, relaxation |
| Consumption | Raw cannabis, juicing | Vaporization, edibles |
Ultimately, the choice between THCA and THC comes down to individual goals and desired outcomes. For those looking to explore the therapeutic benefits without the intoxicating effects, THCA may be the perfect candidate. Conversely, THC serves those seeking a recreational experience or specific psychoactive benefits.Understanding these differences can empower consumers to make informed decisions suited to their needs.
Therapeutic Benefits of THCA and THC
when it comes to therapeutic applications, both THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) and THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) present distinct advantages. their unique chemical structures lead to varying effects on the body that are especially notable in the context of treating various health conditions.
THCA is often lauded for its non-psychoactive qualities, making it a favorable option for medical treatment without the intoxication associated with its decarboxylated counterpart, THC. Research suggests that THCA may offer benefits such as:
- Anti-inflammatory properties that can assist individuals suffering from chronic pain and immune disorders.
- Neuroprotective effects which might aid in conditions like Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
- Appetite stimulation, providing relief for those undergoing treatments that cause loss of appetite, such as chemotherapy.
On the other hand, THC is known for its psychoactive effects and provides a different array of therapeutic advantages. Its capacity to produce a ”high” can help in specific medical scenarios, leading to benefits such as:
- Pain relief through its analgesic properties, making it useful for patients with severe pain.
- Anxiety reduction by managing stress and providing a sense of relaxation for those with anxiety disorders.
- Muscle relaxation, effectively aiding individuals dealing with conditions like multiple sclerosis.
the diverse pharmacological profiles of THCA and THC highlight the importance of tailoring cannabis treatments to individual needs. Below is a simplified comparison of the two compounds:
| Component | Effects | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| THCA | Non-psychoactive, Anti-inflammatory | Chronic pain, Neuroprotection |
| THC | Psychoactive, Pain relief | Severe pain, Anxiety management |
Consumption Methods: What You Need to know
When exploring the engaging world of THCA and THC, understanding the consumption methods available is crucial. Each method offers distinct experiences,effects,and potencies,making the choice highly personal and important. Here are some popular options to consider:
- Vaping: This method involves heating cannabis oil,allowing users to inhale the active compounds without combustion. It preserves terpenes, enhancing flavor while providing efficient absorption of both THCA and THC.
- Edibles: Infused foods and beverages provide a longer-lasting effect. Though, THCA must first be decarboxylated to convert into THC for maximum potency in these products.
- Topicals: While mostly used for localized relief, certain topicals utilize THCA’s anti-inflammatory properties.They don’t create the psychoactive effects commonly associated with THC.
- Tinctures: Concentrated liquid extracts can be taken sublingually for fast onset. Tinctures unlocking the potential of both THCA and THC can create a customizable experience tailored to individual preferences.
Each of these methods not only affects the potency and onset of effects but also the overall experience of consuming cannabis products. Factors such as dosage, individual tolerance, and desired effects should all be considered when choosing your consumption method. As a notable example, those seeking immediate relief may prefer vaping or tinctures, while those looking for a more prolonged effect might gravitate toward edibles.
Here’s a quick comparison of the primary consumption methods:
| Method | Onset Time | Duration | Psychoactive Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vaping | Immediate | 1-3 hours | Yes |
| Edibles | 30-90 minutes | 4-8 hours | Yes |
| Topicals | Variable | Localized | No |
| Tinctures | 15-45 minutes | 4-6 hours | Yes |
Choosing the right method for consuming cannabis can greatly influence your experience. Experimenting with different methods will reveal what works best for you and your body’s unique chemistry, enhancing both enjoyment and therapeutic benefits.
Selecting the Right Cannabis for Your Needs
When navigating the world of cannabis,particularly the distinct properties of THCA and THC,it’s crucial to align your selection with your personal needs and goals. Many consumers are becoming increasingly aware of the specific effects each compound offers. Understanding the subtleties of these cannabinoids can make a significant difference in your overall experience.
Before making a choice, consider the following factors:
- Desired Effects: Are you seeking relaxation, pain relief, or perhaps an uplifting mood? THCA is known for its non-psychoactive and therapeutic properties, making it suitable for those looking to experience medicinal benefits without the high.
- Consumption method: How do you prefer to consume your cannabis? While THCA is often found in raw forms, like tinctures and edibles, THC can be enjoyed through smoking, vaping, or dabbing. Your preferred method can influence which option works best for you.
- Tolerance Level: Understanding your tolerance to THC is essential. If you are sensitive to psychoactive effects, opting for THCA products may be more enjoyable, as they provide the benefits without the high.
To illustrate the distinct differences, consider the following table that summarizes the key attributes of THCA and THC:
| Cannabinoid | potency | Psychoactivity | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| THCA | Low | Non-psychoactive | Anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective |
| THC | High | Psychoactive | Euphoric, analgesic, appetite stimulant |
By taking the time to understand these aspects, you can make informed decisions that enhance your cannabis experience. Whether you lean towards the therapeutic profile of THCA or the broad psychoactive effects of THC,knowing what you seek in terms of wellness can lead to a more satisfying and tailored cannabis journey.
Key Takeaways
In the ever-evolving landscape of cannabis, understanding the nuanced differences between THCA and THC is pivotal for both enthusiasts and newcomers alike. As we’ve explored, the journey from raw plant to the high-THC products on dispensary shelves is marked by change, both chemical and experiential.While THC captivates with its psychoactive prowess, THCA stands as a testament to the untapped potential of cannabis in its natural state, offering a range of therapeutic benefits without the high.
As research continues to delve deeper into these compounds, it’s clear that the conversation surrounding cannabis is just beginning. By arming ourselves with knowledge about THCA and THC, we not only enhance our appreciation of this complex plant but also empower ourselves to make informed choices that align with our individual needs and preferences. Whether you’re seeking relief, relaxation, or a spirited exploration of cannabis culture, understanding the roles of these compounds is essential.
So, as you embark on your own cannabis journey, take a moment to ponder the full spectrum of opportunities that the plant has to offer. Both THCA and THC have their place in this rich tapestry, inviting us to discover and embrace the multitude of experiences waiting to be unveiled. Here’s to informed choices and a deeper connection to the world of cannabis.