Title: The Potency Puzzle: Understanding THCA and Its Effects
as the world of cannabis continues to evolve,so too does the conversation surrounding its myriad compounds. among these,tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) stands out,intriguing both enthusiasts and researchers alike. While many are familiar with its more famous counterpart, THC-known for its psychoactive properties-THCA often remains shrouded in mystery.This article seeks to unravel the potency question surrounding THCA. Is it a hidden gem with therapeutic potential, or merely a precursor to the rush of THC? Together, we will explore the science behind this fascinating compound and examine its potential effects, drawing from emerging research and anecdotal evidence. Join us on this journey as we discover what makes THCA unique and how it fits into the broader landscape of cannabis potency.
Understanding THCA and Its Chemical Properties
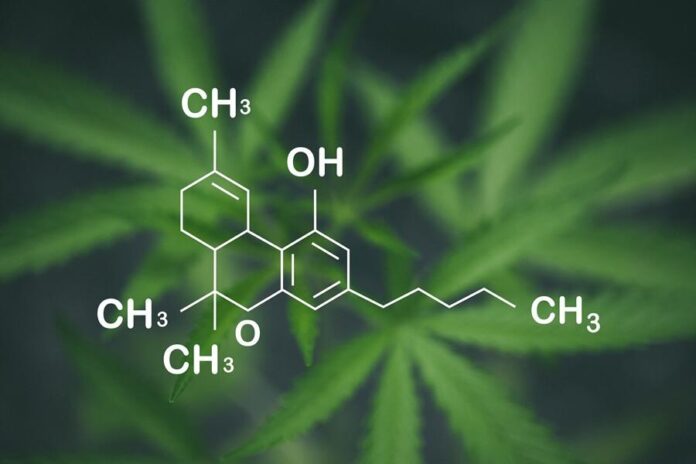
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in raw cannabis. It is the precursor to THC, the well-known compound responsible for the psychoactive effects of marijuana. Understanding THCA’s chemical properties is essential for anyone curious about its potential benefits and uses. This compound dissolves well in organic solvents and is typically stable under standard conditions, which makes it ideal for a variety of applications, including oils and tinctures.
The molecular formula of THCA is C22H30O4, featuring a unique structure that provides it with distinct properties compared to its decarboxylated counterpart, THC. This structure allows THCA to engage in various biochemical interactions within the body, which are still being researched.Some notable aspects include:
- Non-psychoactive: unlike THC,THCA does not produce a high.
- Potential therapeutic effects: Preliminary studies suggest it may have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties.
- Stability: THCA retains its potency when stored correctly,making it an appealing option for cannabis enthusiasts.
As cannabis continues to gain acceptance as a potential medical treatment, more attention is being paid to compounds like THCA.The understanding of its properties is crucial for consumers looking to explore its benefits without the psychoactive effects associated with THC. Emerging research may soon reveal a wealth of possibilities for utilizing THCA in therapeutic contexts, and as scientists delve deeper into its potential, the future of this cannabinoid looks promising.
Exploring the Psychoactive Nature of THCA
The exploration of THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) unveils a fascinating facet of cannabis that diverges from the commonly discussed THC. Unlike its decarboxylated counterpart, THCA is non-psychoactive in its raw form, meaning that it does not produce the euphoric effects typically associated with cannabis consumption. This characteristic has piqued the interest of researchers and consumers alike, as it opens up a realm of benefits without the intoxication. The allure of THCA lies in its potential to offer therapeutic advantages devoid of the high, attracting individuals seeking relief from various ailments.
As we delve deeper,we uncover a variety of potential benefits that may accompany THCA consumption. Some of the more promising areas of research highlight its possible roles in:
- Neuroprotective properties: Initial studies suggest that THCA may help protect nerve cells and support overall brain health.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: THCA may reduce inflammation, making it a candidate for treating conditions like arthritis and other inflammatory disorders.
- Antiemetic activity: For those experiencing nausea and vomiting, especially from chemotherapy, THCA might offer relief without psychoactive side effects.
though research is still in its infancy,the utilization of THCA may evolve as consumers seek out products that provide wellness without the “high.” The differentiation between THCA and THC underscores a crucial aspect of cannabis: its complexity. To visualize the difference in potency and effects between THCA and THC, consider the following comparison:
| Compound | psychoactive Effects | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| THCA | No | Anti-inflammatory, Neuroprotective |
| THC | Yes | Euphoric, Analgesic |
Comparing THCA Potency to Other Cannabinoids
When it comes to understanding the potency of THCA, it’s crucial to place it alongside other well-known cannabinoids such as THC and CBD. While THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, its potency in the raw, unprocessed cannabis plant can often be underestimated. Unlike THC, which can produce intoxicating effects, THCA is gaining attention for its potential therapeutic benefits without the high. This key distinction makes THCA particularly appealing to users seeking the medicinal properties of cannabis without psychoactive effects.
The potency comparison between THCA and other cannabinoids can be illustrated through a basic table that highlights the active forms and effects:
| cannabinoid | Type | Potency | Psychoactive Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| THCA | Acid form | Moderate | No |
| THC | Decarboxylated | High | Yes |
| CBD | Neutral | Variable | No |
Moreover, the effects of THCA are believed to contribute positively to a range of health conditions. While research is still emergent, users have reported benefits including inflammation reduction, appetite stimulation, and neuroprotective properties. These potential uses offer a counterpoint to the complexities associated with THC, where the experience can vary widely among individuals. As the cannabis industry evolves, so does the understanding of how different cannabinoids, including THCA, administer their respective effects, making it essential for both consumers and researchers alike to keep abreast of these developments.
The Role of Decarboxylation in THCA’s Effects
Decarboxylation is a critical chemical reaction that substantially influences the effects of various cannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA). This process involves the removal of a carboxyl group from the acidic precursor molecule, converting THCA into THC, the compound notorious for its psychoactive properties. While THCA itself is non-intoxicating, the conversion into THC can enhance the overall therapeutic effects experienced by the user. Understanding this transformation is essential for appreciating the potential benefits of THCA.
Several factors influence the decarboxylation process, which include:
- Temperature: Higher temperatures typically accelerate decarboxylation, making the process more efficient.
- Time: Extended exposure to heat can ensure more complete conversion from THCA to THC.
- Method of consumption: Smoking or vaporizing cannabis can rapidly decarboxylate THCA, unlike edibles where the process may be slower.
The implications of decarboxylation are meaningful for both medical and recreational users. For those seeking relief from conditions such as inflammation, anxiety, or nausea, THCA may be beneficial in its raw form without the psychoactive effects of THC.Conversely, users looking for the euphoric effects of THC will benefit from decarboxylated products. Thus, understanding the role of decarboxylation helps consumers choose the right cannabis products to meet their specific needs, maximizing the potential benefits while minimizing unwanted effects.
Potential therapeutic benefits and Uses of THCA
The (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) have garnered attention in recent years, primarily due to its non-psychoactive properties and its role as a precursor to THC. while many consumers and researchers are more familiar with THC, current studies suggest that THCA may offer an array of health benefits that could be quite impactful.
Research indicates that THCA may exhibit anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, making it a candidate for addressing conditions such as:
- Chronic pain
- Autoimmune diseases
- Neurodegenerative disorders
Moreover, THCA is potentially beneficial in managing nausea and stimulating appetite without the psychoactive effects associated with THC, appealing to patients undergoing treatments such as chemotherapy. This makes it an interesting option for those seeking relief while maintaining clarity and functionality.The exploration of THCA in clinical applications is still in its infancy, but preliminary data point towards a promising future for this cannabinoid.
Practical Recommendations for Consumption and Extraction
When exploring the potential benefits of THCA, it’s essential to consider how to consume and extract it effectively. Keeping in mind that THCA is non-psychoactive in its raw form, individuals seeking medical or therapeutic benefits should focus on methods that preserve its properties. Here are some practical recommendations:
- Raw Consumption: Incorporate raw cannabis leaves into smoothies or salads to directly benefit from THCA without any psychoactive effects.
- Juicing: Extract juice from fresh cannabis flowers or leaves, which allows for high levels of THCA while also delivering a wide array of nutrients.
- Cooking: When cooking, lower temperatures preserve THCA; consider using it in dressings or light sautés rather than high-heat methods.
For those interested in extraction, understanding the right techniques is crucial to maintain the integrity of THCA. Common methods used in the extraction process include:
| Extraction Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Press | Retains THCA & nutrients | Time-consuming |
| Solvent Extraction | High yield | May require complex safety measures |
| CO2 Extraction | Highly efficient | Requires expensive equipment |
Ultimately, integrating THCA into your wellness routine can be beneficial, but careful consideration of methods is essential. Always prioritize quality and organic sources of cannabis for extraction, and consult with professionals if you are unsure about the processes involved. Embracing these practices will not only enhance your experience but also ensure you are harnessing the full potential of THCA.
Future Outlook
In the realm of cannabis, the exploration of compounds like THCA invites both curiosity and caution. As we’ve seen,the potential potency of THCA varies widely,influenced by a multitude of factors ranging from the strain of the cannabis plant to the method of consumption. While it may not deliver the psychoactive effects of its decarboxylated counterpart, THC, THCA holds promise for a range of therapeutic applications that warrant further investigation.
as the landscape of cannabis research continues to evolve, so too will our understanding of THCA’s capabilities. For those intrigued by the possibilities of this intriguing compound, the journey doesn’t end here. Staying informed and open to new discoveries could unlock insights that reshape how we approach both cannabis and health. Ultimately, whether you’re a seasoned enthusiast or a curious newcomer, the conversation surrounding THCA-and its potential potency-will undoubtedly unfold in fascinating ways in the years to come.