In the ever-evolving world of cannabis, terminology can ofen be a source of confusion, particularly when it comes to the myriad of compounds derived from the plant. Among those sparking curiosity are THCA rosin and THC, two substances that play pivotal roles in the cannabis experience. While they share similar names and origins, their chemical structures and effects diverge considerably. This article delves into the distinctions and connections between THCA rosin and THC, demystifying the science behind these compounds and shedding light on what they mean for consumers, patients, and enthusiasts alike. Join us as we explore the fascinating nuances that set these two components apart, and discover whether they are truly the same—or profoundly different.
Understanding THCA Rosin and THC: A Closer Look at Cannabinoids
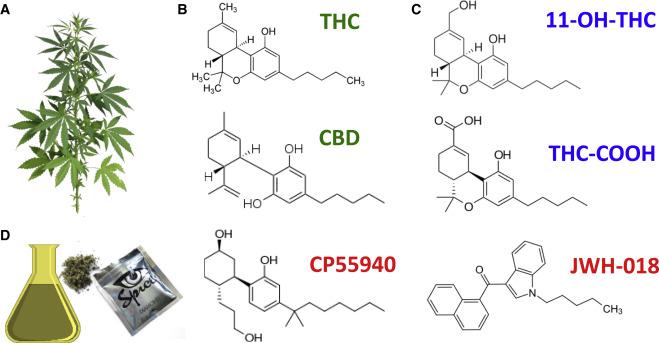
to understand the relationship between THCA rosin and THC, it’s essential to delve into the nature of cannabinoids. THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is a non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis plants, typically present in high concentrations in raw, unprocessed marijuana. On the other hand, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is the well-known psychoactive element responsible for the euphoric “high” associated with cannabis consumption. The conversion between THCA and THC occurs through a process called decarboxylation, which usually happens when cannabis is heated, such as in smoking or cooking methods.
THCA rosin is a concentrated form of THCA extracted from cannabis flowers using a solvent-free technique that involves heat and pressure. It retains much of the plant’s original terpenes and cannabinoids, providing a full-spectrum experience without transitioning into THC. This characteristic allows users to experience potential medicinal benefits without the intoxicating effects.The rosin extraction process effectively captures the properties of the plant while avoiding unwanted chemicals or solvents. Some benefits of THCA rosin include:
- Non-psychoactive experience, making it suitable for therapeutic use.
- Preservation of terpenes, which can enhance flavor and aroma.
- High concentrations of THCA, offering potent effects for medicinal applications.
When comparing THCA rosin to THC in terms of health properties and usage, their distinct effects warrant attention. While both compounds share therapeutic potential, such as anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, they engage with the body differently. For those interested in the non-psychoactive benefits of cannabis, THCA rosin emerges as a promising option. Below is a simple representation of their key differences:
| Aspect | THCA Rosin | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactivity | Non-psychoactive | Psychoactive |
| Extraction Method | Solvent-free rosin press | Various methods including solvents |
| Therapeutic Use | Medicinal potential without high | often used recreationally |
the Unique Properties of THCA Rosin: Unraveling the Science Behind the Extract
THCA rosin is an intriguing substance that stands out due to its unique composition and extraction method.Unlike traditional THC, which is typically derived from the decarboxylation of CBDA or THCA, THCA rosin retains its acidic form and is produced through a solventless extraction process that employs heat and pressure. This method not only preserves the integrity of the cannabinoids but also maintains the full spectrum of terpenes, contributing to a more robust flavor profile and potential therapeutic benefits. Some of the key properties of THCA rosin include:
- Solventless Extraction: This method ensures that no harmful chemicals or solvents compromise the purity of the extract.
- Acidic Cannabinoids: THCA rosin remains in its non-psychoactive form, offering a different experience compared to traditional THC.
- Full-Spectrum Benefits: The entrapment of terpenes enhances the entourage effect, possibly amplifying the therapeutic properties of the cannabinoids.
When we compare the profiles of THCA and THC, it’s fundamental to understand their chemical structures and effects. THCA is a precursor to THC, and through decarboxylation (usually via heat), it converts to THC, which produces psychoactive effects. The table below showcases the differences between the two:
| Property | THCA | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Psychotropic Effect | Non-Psychoactive | Psychoactive |
| Extraction Method | Rosin (solventless) | Can be solvent-based |
| Medical Usage | Anti-inflammatory, Neuroprotective | Relief of pain, Euphoria |
Beyond their chemical dichotomy, the implications of using THCA rosin can be substantial for those seeking therapeutic benefits without the psychoactive side effects typically associated with THC.Researchers are beginning to delve deeper into the potential advantages of utilizing THCA in various applications, exploring topics such as cannabinoid receptors, inflammation, and overall wellness. The intricate dance of cannabinoids and terpenes within THCA rosin may hold the key to unlocking new pathways for achieving holistic health.
Comparative Analysis: Effects of THCA vs. THC on the Body and Mind
When exploring the effects of THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) versus THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), it’s essential to consider their distinct properties. THCA is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, meaning it does not produce the intoxicating high commonly associated with cannabis. this difference significantly influences how each compound interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system. While THC binds primarily with the CB1 receptors in the brain, exerting psychoactive effects, THCA’s interaction is far less pronounced, frequently enough leading to therapeutic benefits with minimal mental alteration.
The therapeutic potential of both compounds varies widely, making them suitable for different applications.some of the documented effects of THCA include:
- anti-inflammatory properties: Potential relief for conditions like arthritis.
- Neuroprotective effects: May help in preserving brain health.
- Anti-nausea benefits: Often sought by those undergoing chemotherapy.
On the other hand,THC is widely recognized for its:
- Psychoactive effects: Inducing euphoria and altering perception.
- increased appetite: Commonly referred to as the “munchies.”
- Potential anxiety or paranoia: Can exacerbate symptoms in sensitive individuals.
| Characteristic | THCA | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactivity | No | Yes |
| Medical Benefits | Anti-inflammatory, Neuroprotective | pain relief, Appetite stimulation |
| Conversion | Can convert to THC through decarboxylation | Already psychoactive |
Ultimately, the choice between THCA and THC will depend on individual needs and circumstances, as each compound offers unique benefits and potential drawbacks. Understanding their specific effects helps consumers make informed decisions tailored to their health and wellness goals.
Culinary and Medicinal Uses of THCA Rosin: Exploring Practical Applications
THCA rosin, the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, is gaining traction not only for its potential benefits in the field of cannabis but also for its versatile applications in both culinary and medicinal contexts. Chefs and home cooks alike are beginning to recognize the unique qualities of THCA rosin, using it to enhance flavor and health benefits in various dishes. It can be incorporated in methods such as:
- Baking: Infuse brownies or cookies for a gourmet twist.
- Salad Dressings: Mix with oils to create a premium dressing packed with potential benefits.
- Sauces and Dips: Enhance homemade sauces for a richer flavor profile.
On the medicinal side, THCA rosin offers an array of potential therapeutic benefits, prompting interest among wellness enthusiasts and health professionals. Anecdotal evidence suggests that THCA may help with:
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Reducing inflammation may aid in managing chronic conditions.
- Neuroprotective Properties: Potentially beneficial for neurodegenerative disorders.
- Nausea relief: Aiding those undergoing treatments like chemotherapy.
For those looking to incorporate THCA rosin into a healthy lifestyle, understanding its applications and implications can be quite valuable. As more culinary experts and healthcare practitioners explore this fascinating compound, the future of THCA rosin promises an exciting blend of flavors and health benefits that can elevate both the dining experience and wellness routines.
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Considerations for THCA products
When it comes to THCA products, navigating the legal landscape can be a complex task. As laws surrounding cannabis continue to evolve, understanding the distinctions between THCA and THC is paramount for consumers and producers alike. Key regulations typically focus on factors such as the specific content of tetrahydrocannabinolic acids, the extraction methods used, and the intended use of the product. Therefore, it is crucial for businesses to maintain compliance with local laws to avoid potential fines and legal complications.
Different jurisdictions may have varying standards for what constitutes legal THCA products. In many places, THCA is viewed differently from its decarboxylated form, THC. In this very way, it is indeed essential for stakeholders in the industry to stay informed on:
- State-specific cannabis legislation: Understanding the specific regulations in your state or region.
- Product labeling requirements: ensuring that all products are accurately labeled with their contents and potential effects.
- Testing protocols: Conducting third-party lab tests to verify the composition and safety of THCA products.
To further illustrate the differences in legal treatment between THCA and THC, consider the following table that summarizes common regulations:
| Aspect | THCA | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Status | Generally considered non-psychoactive. | Regulated as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions. |
| Usage | used in raw cannabis products and non-psychoactive therapies. | Commonly used in recreational and medicinal cannabis products. |
| Testing Requirements | May require different testing criteria. | Subject to stringent quality and safety standards. |
Consumption Methods: Finding the Right Approach for THCA Rosin and THC
When it comes to enjoying THCA rosin and THC, selecting the right consumption method can significantly enhance your experience. Each approach carries its own benefits and can greatly affect the potency and flavor of the product. Here are some popular consumption methods to consider:
- Vaporization: This method heats cannabis extract until the desired compounds are released as vapor. Vaporizing THCA rosin or THC preserves the terpenes, providing a rich flavor profile while minimizing harmful byproducts.
- Edibles: Incorporating THCA rosin into edibles can be a delightful way to experience its effects. Carefully managing dosage is essential, as the onset of effects may take longer, but they can be more intense and longer-lasting.
- Dabbing: This technique involves using a dab rig to inhale concentrated extracts. Dabbing THCA rosin delivers a potent hit that provides immediate effects, making it a favorite among seasoned users.
For those looking for a more traditional experience, joints and blunts can be infused with THCA rosin or THC concentrates. This combination not only enhances the flavor but also allows consumers to enjoy the familiar ritual of smoking.You may also consider cooking and baking, where extracts can be mixed into various recipes, offering a creative way to consume your favorite products.
Below is a concise comparison of the effects and characteristics associated with each method:
| Consumption Method | onset Time | Potency Level | Flavor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vaporization | Immediate | Moderate to High | Rich and terpene-heavy |
| Edibles | 30 mins – 2 hours | Moderate to High | Varied, depending on ingredients |
| Dabbing | Immediate | Very High | Concentrated and Bold |
| Joints/Blunts | Immediate | moderate | Classic Cannabis Flavor |
| Cooking/Baking | 30 mins – 2 hours | Varies | Dependent on the Recipe |
The Way Forward
while THCA rosin and THC share a close relationship, they are not identical substances. THCA rosin, the raw, non-psychoactive form, offers its own unique benefits and potential therapeutic properties, distinguishing it from its decarboxylated counterpart, THC, known for its euphoric effects.As cannabis research continues to evolve, understanding these differences becomes increasingly essential for consumers and patients alike. Whether you’re seeking the psychoactive experience of THC or the therapeutic promise of THCA rosin, informed choices can empower your cannabis journey.Ultimately, the world of cannabinoids is rich and nuanced, inviting curiosity and exploration as we unlock the full potential of this remarkable plant.