In the ever-evolving landscape of cannabis research, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) stands out as a lesser-known yet intriguing compound. As the raw, unheated precursor to the well-known psychoactive THC, THCA has garnered attention not only for its potential therapeutic benefits but also for its impact on the understanding of cannabis’ effects on the human body. This article aims to demystify THCA, examining its unique properties, potential benefits, and the ongoing discussions surrounding its addictive nature. By delving into the science behind THCA,we seek to shed light on its role within the broader cannabis spectrum and contribute to the growing conversation about substance use and addiction. Join us as we navigate the complexities of this fascinating compound and explore what makes it both a valuable resource for some and a source of concern for others.
Understanding the Basics of THCA and Its chemical Structure
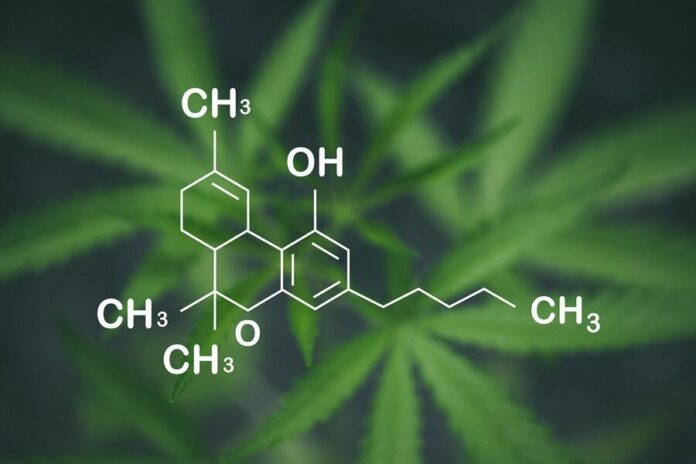
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis plants. It serves as the precursor to THC, the well-known psychoactive component responsible for the “high” associated with marijuana. The chemical structure of THCA is represented by a molecular formula of C22H30O4, illustrating its composition of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Its structure is characterized by a carboxylic acid functional group, which plays a significant role in its interaction with the body’s endocannabinoid system.
Understanding THCA’s molecular structure reveals several vital features that contribute to its effects. The compound consists of a long carbon chain with a series of double bonds that influence its reactivity and biological activity. When heated,THCA undergoes decarboxylation,a reaction that removes a carboxyl group,transforming it into THC. This transformation is essential for users seeking psychoactive effects, as THCA itself does not bind well to cannabinoid receptors. The ability to convert to THC through processes like smoking or vaping is what makes THCA notably interesting in cannabinoid research.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H30O4 |
| Psychoactivity | Non-psychoactive |
| Conversion | transforms into THC upon heating |
the implications of THCA extend beyond mere chemical interactions; it may have therapeutic potential that deserves attention. Research suggests that THCA may offer anti-inflammatory properties, neuroprotective effects, and anti-emetic capabilities without producing the euphoric effects typically associated with THC. This unique profile opens up discussions regarding its use in medicinal applications for patients who wish to avoid the psychoactive side effects while still benefiting from cannabis’s potential therapeutic effects.
The Therapeutic Potential of THCA: benefits Beyond the High
The exploration of THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) offers a unique perspective on cannabis that diverges from conventional THC narratives. Unlike its psychoactive counterpart, THCA presents a range of therapeutic advantages without inducing the intoxicating “high.” This property is particularly significant for individuals seeking the potential benefits of cannabis without the alteration of consciousness. Research indicates that THCA might play a role in addressing various health concerns such as:
- Anti-inflammatory effects: THCA has shown promise in reducing inflammation, which coudl benefit conditions like arthritis or autoimmune disorders.
- Neuroprotective properties: Preliminary studies suggest that THCA might protect the nervous system, possibly aiding in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Anti-nausea effects: this cannabinoid could help alleviate nausea,making it a useful option for patients undergoing treatments like chemotherapy.
Furthermore, the consumption of THCA-rich products has become increasingly popular in the wellness community, prompting an interest in various forms of intake. From raw cannabis juices to dietary supplements, these products are celebrated not only for their health benefits but also for their versatile applications. When comparing THCA to its activated relatives, a table highlighting their differences can elucidate the unique qualities of THCA:
| Component | Psychoactive | Therapeutic Benefits | Common Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| THCA | No | Anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-nausea | raw cannabis, tinctures |
| THC | Yes | Pain relief, appetite stimulation | Flower, edibles |
As we continue to unveil the complexities of cannabis compounds, the recognition of THCA’s healing potential becomes vital for both medical practitioners and patients alike. The non-psychoactive nature of THCA does not diminish its efficacy; rather, it emphasizes a need for choice therapies that can accommodate a broader spectrum of users. Looking forward, further research may pave the way for THCA to be integrated into a more extensive array of treatment options, underscoring its role in the burgeoning field of cannabis research.
Distinguishing THCA from THC: Is There an Addictive Link?
When diving into the world of cannabis compounds, differentiating between THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) is essential for understanding their effects and potential for addiction.THCA is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, meaning it does not produce the euphoric “high” typically associated with cannabis use. This distinction is crucial because it suggests different implications for dependency and addiction. While THC can lead to psychoactive experiences, it is not immediately clear whether THCA shares any addictive potential.
Research on the addictive nature of cannabis frequently enough centers around THC as it binds effectively to cannabinoid receptors in the brain. This interaction is linked to the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. In contrast,THCA does not demonstrate the same binding affinity and,therefore,may not activate this reward system in the same manner. To better understand this relationship, consider the following factors:
- Binding Affinity: THCA has a lower binding affinity to cannabinoid receptors compared to THC.
- Psychoactive Effects: THCA is non-psychoactive,reducing the likelihood of dependency.
- Research Status: Limited studies exist on THCA’s addictive properties.
Examining the potential for addiction involves analyzing user patterns and behavioral responses. Although anecdotal evidence suggests a lower risk of dependency with THCA, concerns about the whole cannabis plant and its various compounds remain.The complex interplay of cannabinoids, terpenes, and individual user physiology makes conclusions about addiction challenging. More extensive studies are needed to uncover whether THCA poses any long-term risks or addictive properties.
Exploring the Neurobiological effects of THCA on the Brain
The exploration of THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) illustrates a fascinating intersection between cannabis science and neurobiology. Unlike its psychoactive counterpart THC, THCA does not produce the euphoric effects commonly associated with cannabis consumption. Nonetheless, research suggests that THCA may influence the brain’s endocannabinoid system, engaging with a complex web of receptors that govern various physiological processes. Through interactions with CB1 and CB2 receptors, THCA might contribute minimally to mood regulation and neuroprotection, even though its effects are still being unraveled. This nuance raises questions about the potential therapeutic implications of THCA.
Notably, the neurobiological effects of THCA include:
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Evidence indicates that THCA may help reduce inflammation in the brain, potentially benefiting neurodegenerative conditions.
- Neuroprotection: Some studies suggest THCA might shield neurons from damage, promoting overall brain health.
- Influence on neurotransmitters: THCA may modify the release of neurotransmitters, affecting mood and cognition without the high associated with traditional THC.
To further understand these effects, a brief comparison of THCA and THC’s interactions with the brain is revealing.
| Compound | Effects on Brain | Psychoactive Properties |
|---|---|---|
| THCA | Potential neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory | No |
| THC | Induces euphoria, alters perception | Yes |
While ongoing research is crucial to fully understand the properties of THCA, its unique interaction with the brain raises intriguing possibilities. By exploring its mechanisms, we gain insights into both its therapeutic potential and its capacity to circumvent the addictive traits associated with more well-known cannabinoids.As the fields of neuroscience and cannabis research continue to evolve, THCA stands out as a compound worthy of attention.
Addressing Myths: THCA Use and the Risk of Addiction
The conversation around THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and its potential for addiction frequently enough drifts into the realm of misconceptions. While THCA is a non-psychoactive compound found in raw cannabis, many assume that any cannabis derivative may lead to dependency issues. However, research shows that THCA does not produce the euphoric high typically associated with its more well-known counterpart, THC. Instead, THCA is reputed for its therapeutic benefits without the intoxicating effects, lending credence to the argument that it may not pose the same risk of addiction as THC does.
It’s important to differentiate between *dependence* and *addiction*. Dependence can occur with various substances, including legal ones like caffeine, when the body adapts to their presence. Conversely,addiction is characterized by a compulsive need to seek out the substance despite negative consequences. Here are some critical points to consider:
- Non-Psychoactivity: THCA does not cause a high, reducing the likelihood of developing habitual use.
- Research on Dependency: Current studies indicate that THCA may not activate the brain’s reward system in the same way that THC does.
- Potential Therapeutic Use: THCA may aid with inflammation and nausea without the addictive aspects of traditional THC products.
Furthermore, understanding the biological mechanism of THCA can also help demystify the fear surrounding its potential for addiction. While some cannabinoids bind to the endocannabinoid receptors in the brain, leading to reward responses, THCA interacts differently within the body’s systems. Here’s a simplified comparison:
| Characteristic | THCA | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactive Effects | No | Yes |
| Risk of Addiction | Low | Higher |
| Medical Benefits | Anti-inflammatory, Neuroprotective | Pain Relief, euphoria |
As science continues to explore the nuances of cannabinoids like THCA, it is evident that misconceptions should be addressed with careful research and education. Emphasizing its medical benefits and non-addictive nature can foster a more informed dialog, encouraging individuals to explore THCA without the fear commonly associated with traditional cannabis products.
Practical Recommendations for Safe Consumption of THCA Products
When exploring the world of THCA products, it’s imperative to approach their consumption with care. Consider starting with low doses, as individual tolerances can vary widely. This cautious approach allows your body to adjust and helps you gauge how you respond to the compound. Tracking your experiences in a journal can be beneficial in identifying the effects and timing that work best for you.
Setting the right surroundings for consumption can enhance your experience. It’s recommended to choose a cozy and familiar space where you feel safe and relaxed. Ensure that potential distractions are minimized, as this can help you focus on how the product affects you physically and mentally.Engaging in activities like listening to music or meditating can also complement the experience, fostering a deeper connection with the effects of THCA.
To support informed choices, always purchase THCA products from licensed dispensaries or reputable sources. Look for products that include third-party lab testing, which provides openness regarding cannabinoid concentrations and the presence of any contaminants. Here’s a quick comparison table to help you recognize essential aspects when choosing THCA products:
| Product Type | Potential Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| THCA oil | Easy to dose, versatile use | Strong flavor, potency can vary |
| THCA Flower | Rich strain options, natural experience | May require additional equipment |
| THCA Edibles | Discreet and tasty | Delayed onset, portion control needed |
Closing Remarks
our exploration of THCA reveals a complex and often misunderstood compound that lies at the heart of cannabis science. While much has been made of its potential therapeutic benefits, the question of its addictive nature invites us to delve deeper into the nuances of this enigmatic substance. As researchers continue to dissect the chemical intricacies of cannabinoids, understanding THCA offers a window into the broader conversation about cannabis, addiction, and human health.
As with any substance, knowledge is key. By unraveling the layers of THCA, we empower ourselves to make informed choices that reflect our personal needs and values. Whether you’re a curious newcomer or a seasoned enthusiast, remaining informed and open to new findings will guide us toward a more comprehensive understanding of cannabis in all its forms.
As we navigate the evolving landscape of cannabis research and legislation, let us embrace curiosity and continue to seek out the truths that lie within. Understanding THCA is more than a scientific inquiry; it is indeed a journey into the heart of a plant that has shaped cultures and communities for centuries. The dialogue is far from over,and in the ever-expanding world of cannabinoids,every question opens the door to new possibilities.