In recent years, the landscape of cannabis regulation has undergone a seismic shift, bringing new compounds and cannabinoids into the spotlight. Among these, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) has emerged as a subject of growing interest and intrigue.Unlike its more famous counterpart, THC, THCA is non-psychoactive in its raw form, yet it holds significant potential for therapeutic benefits. As curiosity surrounding cannabis continues too rise, so too does the complexity of its legal status. With varying regulations across different jurisdictions, understanding the legal framework surrounding THCA is essential for consumers, advocates, and legislators alike. This article seeks to unravel the nuances of THCA’s legal status, examining the current laws, potential implications, and what the future may hold for this enigmatic compound in the realm of cannabis legislation.
Understanding THCA: The Basics and Its Distinction from THC
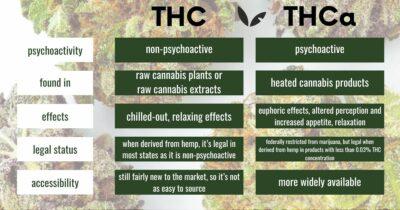
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a naturally occurring compound found in cannabis plants, diverging substantially from its more famous cousin, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). While both compounds share a common molecular structure, they serve distinct roles and exhibit unique properties. THCA is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not produce the euphoric high typically associated with cannabis. To experience the psychoactive effects, THCA must undergo a process called decarboxylation-usually achieved through heat-which transforms it into THC.
The biochemical journey of THCA highlights its potential therapeutic benefits. Research suggests that THCA may possess anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-emetic properties without imparting the psychoactive effects of THC. This makes THCA appealing for those seeking the medicinal benefits of cannabis without becoming intoxicated. As public interest in cannabis grows, understanding these differences becomes essential for both consumers and lawmakers alike.
The legal status of THCA remains a complex issue. In regions where cannabis is legalized, THCA is often treated differently than THC. Regulatory frameworks typically focus on the psychoactive properties of cannabis products, which means that while THC might be restricted, THCA can sometimes be permissible.This distinction plays a significant role in discussions surrounding cannabis legalization,medical use,and the rights of consumers.
To clarify the differences between THCA and THC, consider the following table:
| Aspect | THCA | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactive | No | Yes |
| Common Uses | Therapeutic (anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective) | Recreational and therapeutic |
| Legal Status | Varies by jurisdiction | Highly regulated in many areas |
| Conversion | Requires heat (decarboxylation) | Directly active |
As the cannabis sector evolves, the nuanced understanding of compounds like THCA and THC will be vital for ongoing debates around legalization, safety, and consumer products. By drawing clear distinctions between these compounds, stakeholders can better navigate the changing legal landscape and foster informed dialog about cannabis use.
The Legal Landscape: How THCA Fits into Cannabis Regulations
The intersection of THCA and cannabis regulations is a complex territory that varies significantly across jurisdictions. Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is often misunderstood; while it is a precursor to THC, its legal status can take on a life of its own depending on local law.In many regions, THCA is not explicitly classified under the same legal frameworks as its active form, THC, which is wholly responsible for psychoactive effects. understanding this distinction is essential for individuals and businesses navigating the cannabis regulatory environment.
In the United States, the legal treatment of THCA frequently enough hinges on the Farm Bill of 2018, which legalized hemp-derived compounds with low THC content. The nuances in the definition of hemp play a critical role here. cannabis plants with less than 0.3% THC are generally classified as hemp, making a range of cannabinoids, including THCA, legally permissible. However, state-level regulations can complicate this picture:
| State | THCA Legal Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| California | Legal | Regulated under cannabis laws |
| Texas | Legal | Must be derived from hemp |
| Florida | Legal | Non-psychoactive variant permitted |
Besides legislative differences, public perception is also significant.The cannabis industry relies heavily on consumer education to clarify the benefits and potential uses of THCA. From wellness products to supplements, the market for non-psychoactive cannabinoids is expanding rapidly. Companies engaged in this space must remain compliant with regulations while effectively communicating the differences between THCA and more commonly known cannabinoids. The future of THCA in the cannabis regulatory landscape will likely continue to evolve, reflecting broader changes in cannabis legalization across the nation and beyond.
State-by-State Analysis: Navigating THCA Legislation Across the U.S
As the landscape of THCA legislation continues to evolve,it’s crucial to understand how different states are approaching this cannabinoid.As THCA is non-psychoactive and derived from the cannabis plant, its legal status varies significantly across the United States. Here’s a closer look at how various states are navigating these waters:
| State | THCA Status | Recreational Use | Medical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | Legal | Legal | Legal |
| Texas | Legal (limited) | Illegal | Legal |
| Florida | Legal | Illegal | Legal |
| Ohio | Legal (under strict conditions) | Illegal | Legal |
In states like California, THCA enjoys broad acceptance, falling under the umbrella of both recreational and medical cannabis use.This progressive stance has established a thriving market, encouraging research and consumer access to products that are rich in THCA. Conversely,Texas presents a more restrictive framework,where THCA is legal only in limited forms,primarily for medical use under state-registered programs. Even though recreational use remains illegal, the medical provisions offer some relief for patients seeking cannabinoid-based therapies.
Meanwhile, states such as Florida have fully endorsed THCA for medical purposes, granting patients access to a variety of cannabis-derived products. Though, the same cannot be said for recreational use, which remains prohibited. This divisive approach reflects the broader national dialogue surrounding cannabis and indicates a cautious progress towards acceptance in regions previously known for stricter cannabis regulations.
Other states, like Ohio, adopt a mixed approach, allowing THCA under strict conditions, particularly for registered medical users.This complexity often leaves consumers confused about thier rights and the legal avenues available for THCA use.To navigate these regulations effectively,stakeholders must stay informed about ongoing legislative changes,ensuring they remain compliant while accessing the benefits THCA offers.
Medical Exemptions: THCA’s Role in Therapeutic Contexts
In the evolving landscape of cannabis legality,THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) emerges as a pivotal compound,especially within medical frameworks. Unlike its psychoactive counterpart, THC, THCA remains non-intoxicating and presents a promising therapeutic profile for a variety of medical conditions. This distinction is not merely a scientific curiosity; it profoundly influences legal interpretations surrounding cannabis use in medicinal contexts.
For patients who must navigate stringent legal environments, understanding the exemptions surrounding THCA is vital. Here are a few key medical contexts in which THCA might be considered:
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Research indicates that THCA may help alleviate chronic pain and inflammation, making it beneficial for conditions like arthritis.
- Neuroprotective Effects: early studies suggest that THCA has potential neuroprotective qualities that could be significant for patients suffering from neurodegenerative diseases.
- Appetite Stimulation: THCA may promote appetite without the intoxication associated with THC, providing a safer option for patients undergoing treatments that affect their appetite, such as chemotherapy.
The legal framework surrounding THCA is often complex, as it varies widely by jurisdiction. In some regions, THCA is classified with medicinal benefits, allowing qualified patients to access it without the psychoactive stigma of THC. Table 1 illustrates a few key regions and their legal stances on THCA:
| Region | Legal Status of THCA |
|---|---|
| California | Considered legal for medical use under Prop 215 |
| Canada | Legal in both recreational and medical contexts |
| texas | Legal as a non-psychoactive compound under certain conditions |
As more is understood about THCA’s therapeutic applications, its role in the medical sphere will likely continue to expand. The intersections of law, health, and cannabis are dynamic, and the potential for THCA to provide relief and healing without the psychoactive effects of THC places it at the forefront of discussions surrounding cannabis legislation and patient care.
The Future of THCA: Trends,Challenges,and Legislative Outlook
The landscape surrounding tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is rapidly evolving,driven by shifting public perceptions and an increasing demand for cannabis-derived products. As this compound gains prominence, several trends are emerging:
- Increased Interest in Wellness Products: There is a growing consumer interest in non-psychoactive cannabis products, with THCA being touted for its potential therapeutic benefits, such as anti-inflammatory properties and neuroprotective effects.
- Expansion of Research and Progress: With more universities and institutions studying cannabinoids, the scientific inquiry into THCA’s efficacy and safety is expected to expand, potentially leading to new applications.
- Market Growth: Retail outlets and dispensaries are begining to offer a broader range of THCA products, from tinctures to edibles, catering to consumer demand for versatile options.
Despite its positive trajectory, the future of THCA also presents notable challenges. One significant hurdle is the complex regulatory environment, as existing laws vary widely from state to state. The lack of federal clarity creates an atmosphere of uncertainty that can stifle innovation and investment in the sector. Moreover, educating consumers about the differences between THCA and its psychoactive counterpart, THC, is a crucial challenge that industry stakeholders must address to promote informed purchasing decisions.
The legislative outlook for THCA remains uncertain. Advocates for cannabis reform continue to push for more complete and consistent regulations, which could include:
| Proposed Legislative Changes | potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Decriminalization at Federal Level | Increased legitimacy and market access for THCA products. |
| Standardization of Cannabinoid Regulations | Clearer guidelines leading to enhanced safety and consumer trust. |
| Increased Research Grants | Boosted scientific studies, paving the way for evidence-based product development. |
As the industry forges ahead, the potential for THCA remains vast, but its future will heavily depend on overcoming these challenges while navigating the intricate legal landscape. A collective effort among stakeholders,lawmakers,and consumers will be essential to realize the full potential of this fascinating cannabinoid.
Best Practices for Consumers and Businesses in the THCA Market
as the THCA market continues to grow, both consumers and businesses must navigate its complexities with care. for consumers, it is indeed crucial to understand product labeling and sourcing. Always look for products that provide clear explanations of THCA content, as this can definitely help establish potency and effects.Consider purchasing from reputable vendors who have third-party lab testing available, ensuring that what you’re consuming is safe and accurately represented.
On the business side, establishing clarity is key to building trust with consumers. Companies should implement strict quality control measures and provide accessible information regarding the sourcing of their THCA products. Training staff on the legal nuances surrounding THCA will enable them to better inform customers, further enhancing the consumer experience. Adopting responsible marketing strategies that comply with legal guidelines will protect the brand’s integrity while promoting a positive image within the industry.
Additionally, awareness of local regulations is vital for both consumers and businesses. Various jurisdictions may have different laws regarding THCA; being informed about these can prevent legal pitfalls. A collaborative approach, where businesses engage with local lawmakers and advocacy groups, can lead to a more cohesive understanding of the market. To facilitate this, both parties can utilize resources such as:
- Legal Blogs: Follow industry experts for updates on regulations.
- Local Advocacy Groups: Join groups that focus on cannabis laws.
- Networking Events: Attend industry events to gain insights and share experiences.
For an effective partnership between consumers and businesses,adopting best practices in dialogue is essential. Establish a feedback loop where consumers can share their experiences and businesses can respond with improvements. This mutual engagement creates a dynamic marketplace that fosters both innovation and responsibility, ensuring safety and enjoyment for all involved in the THCA journey.
The Conclusion
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of THCA and its intricate legal status, it becomes evident that this cannabinoid occupies a unique space in the evolving landscape of cannabis regulation. As legislation continues to shift and adapt, so too does the public’s understanding of THCA and its potential benefits.Whether viewed through the lens of law, science, or cultural perceptions, the conversation surrounding THCA is far from over.Navigating the nuances of THCA requires not only legal acumen but also a compassionate understanding of the myriad individuals seeking wellness through its use. As policymakers grapple with the implications of their choices, it is indeed essential to remain informed and engaged, ensuring that laws reflect both scientific advancements and the needs of the community.
In closing, as we venture forward into an era of increased awareness and acceptance, let us remain vigilant in our pursuit of clarity and justice surrounding cannabis laws. The story of THCA is just beginning, and our collective voice can shape its narrative in a way that honors both the plant and the people it serves.