think of THCA as cannabis’s quiet preface – chemically close to the familiar THC but written in a different register. Invisible to the high-seeking eye, THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) lives in raw plant material and many contemporary cannabis products, carrying a story about plant chemistry, consumer choice, and changing laws. Decoding it means tracing a path from molecule to experience, from laboratory bench to bedside or kitchen counter.
This article peels back the layers: how THCA forms in the plant, what happens when heat, time, or processing alter its structure, and how those changes affect what you might expect from a product labeled with THCA. We’ll demystify the science without turning the narrative into a textbook, clarifying key concepts such as decarboxylation, bioavailability, and the relationship between THCA and the body’s endocannabinoid system.
But knowledge alone doesn’t buy the right bottle or bundle.”How to choose” covers the practical decisions consumers face – reading lab reports, comparing product types, and weighing legal and safety considerations – all framed to help you make informed choices rather than prescriptive judgments.
Whether you’re curious about the chemistry, cautious about legality, or simply deciding what to buy, this guide aims to decode THCA into clear, usable information.
THCA Decoded: The Science Behind the Molecule and How It Differs from THC
THCA is the raw, acidic precursor that lives in fresh cannabis plants – a molecule carrying a little carboxyl tail that changes everything. In its native form it is largely non-intoxicatingdecarboxylation. Apply heat (smoking, vaping, baking), and that extra carboxyl group is cleaved off, converting THCA into delta-9-THC, which binds much more readily to CB1 receptors and produces the classic psychoactive effects.
At the cellular level the story is elegant and biochemical: cannabis synthesizes cannabinoids from CBGA through enzyme-driven steps, and THCA synthase is the artisan that crafts THCA before it sits in trichomes awaiting transformation. Emerging studies suggest THCA may have its own bioactivity – reported anti-inflammatory, antiemetic, and neuroprotective actions – but most evidence is preclinical. Regulatory labs and clinicians often treat THCA differently than THC becuase it doesn’t reliably cause intoxication unless converted, which matters for dosing, testing, and product labelling.
When choosing products or experimenting with usage, think about your goal: preserve THCA for therapeutic, non-intoxicating properties, or convert it for psychoactive effects.Practical tips to consider:
- Store raw material cold to slow natural decarboxylation.
- Juicing fresh flowers or leaves preserves THCA and avoids a high.
- Use lab-tested tinctures/flower to know your THCA/THC ratio.
- Be mindful of legal limits – some laws treat THCA differently but may still restrict conversion to THC.
| Property | THCA | THC (Δ9) |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular feature | Contains carboxyl group (-COOH) | Decarboxylated form (no -COOH) |
| Psychoactivity | Non-intoxicating | Intoxicating |
| Activation | Stable in raw plant; converts with heat | Produced by heating or aging |
| Common use | Raw consumption, therapeutic research | Recreational & medical dosing |

A Practical buying and Dosing Guide How to Choose Quality Products Set Safe Dosages and Track Results
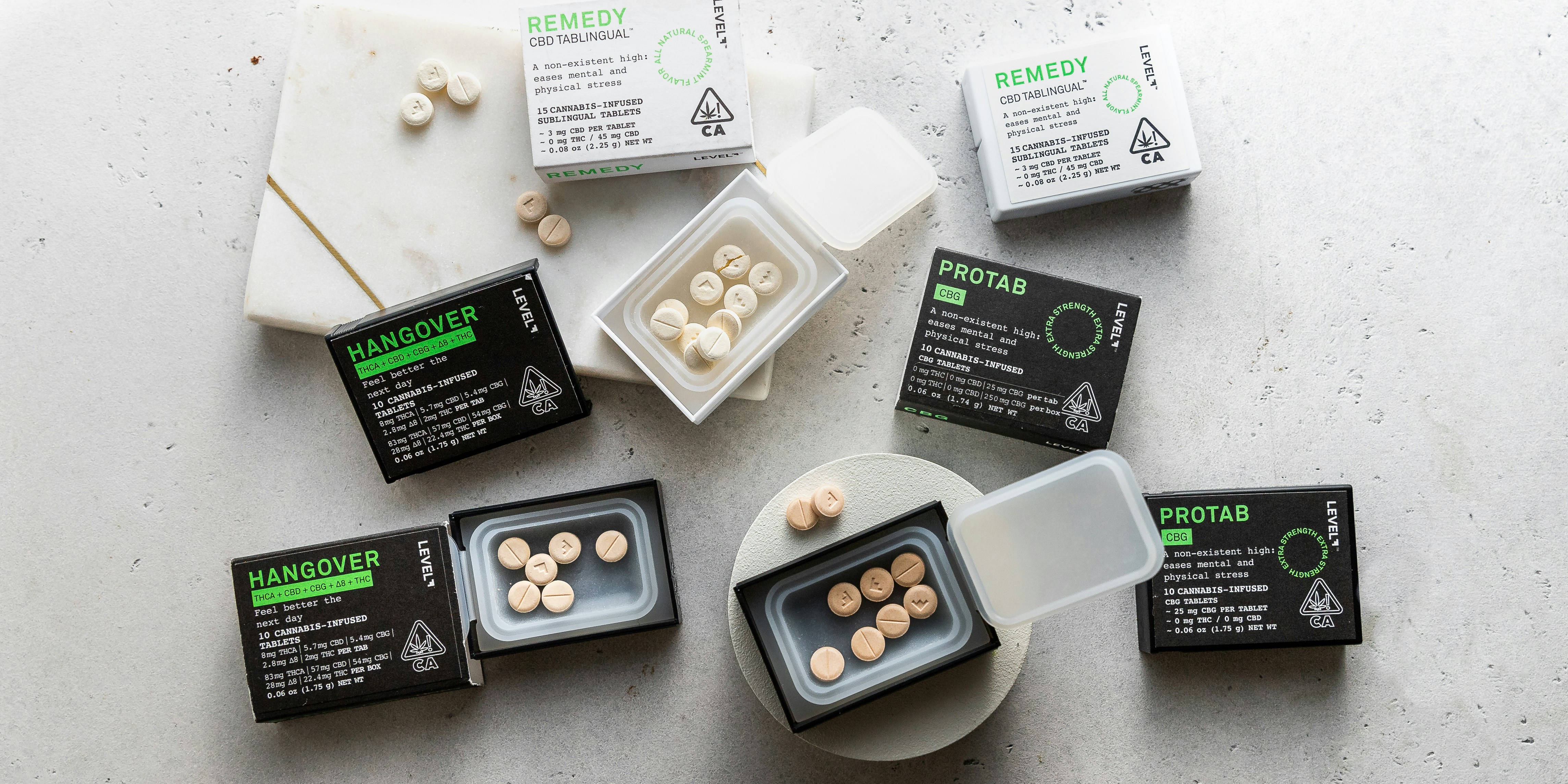
When shopping for THCA products, think like a quality inspector. Prioritize items with a current Certificate of Analysis (COA) that confirms potency and screens for pesticides, heavy metals, and residual solvents. look for clear sourcing-organic hemp or licensed cannabis farms-and transparent extraction methods (CO2 extraction is a reliable benchmark). Choose full-spectrum extracts if you want the entourage affect, or isolates if you need precise dosing with minimal terpenes. Packaging that protects from light and air,and clear labeling (batch number,harvest date,cannabinoid profile) are small details that reveal a brand’s standards.
Start dosing conservatively and adjust methodically. Bioavailability changes by format: inhaled THCA converts quickly and gives faster feedback, while tinctures and edibles take longer but last longer. A “start low, go slow” approach helps you find a agreeable effect without overshooting. Below is a simple reference for starting doses by common formats-use it as a guideline, not a rule, and always round down if unsure.
| Format | Suggested Starter dose | Onset & Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Flower (vaping/smoking) | 1-2 puffs (~2-5 mg) | Onset: minutes • Duration: 1-3 hours |
| Tincture (sublingual) | 0.5-1 full dropper (~2.5-5 mg) | Onset: 15-45 min • Duration: 4-6 hours |
| Edible | 2.5-5 mg | Onset: 45-120 min • duration: 6-10+ hours |
| Topical | Spot test (small amount) | Onset: 15-60 min • Localized effects |
Track every trial like a scientist: log date, time, product name and batch, exact dose, method, setting, and subjective effects. Use a simple notebook or a habit-tracking app-consistency of record beats complexity. Note side effects, duration, and whether you combined other substances or medications. If you see persistent adverse reactions, scale back and consult a healthcare professional. store products cool and dark, rotate stock by harvest date, and keep them out of reach of children and pets to preserve potency and safety.
Final Thoughts
As the curtain falls on THCA decoded, the picture should feel less like a riddle and more like a map. THCA is simply cannabis in an earlier chemical state – a non‑intoxicating acidic precursor that can convert to THC with heat, and whose potential effects and uses depend on product form, extraction method, and individual needs.
when choosing THCA, prioritize transparency: look for third‑party lab results, clear labeling (THCA vs. delta‑9 THC), reputable sourcing, and an extraction method that matches your priorities (whole‑plant vs isolate). Consider how you plan to use it – raw tinctures and flower differ from concentrates and edibles in both effect and legal status – and remember dosing practices like “start low, go slow.” above all, check local laws and, if you have health conditions or take medications, consult a healthcare professional before trying new cannabinoids.
THCA isn’t a miracle cure nor a one‑size‑fits‑all recreational substitute; it’s another tool in a growing pharmacopoeia of cannabis constituents. Armed with the basics of how it effectively works, how it’s labeled, and what to look for in a product, you’re better placed to make choices that are informed, safe, and suited to your goals.
If curiosity persists, let it be guided by evidence, testing, and thoughtful experimentation – and you’ll find that decoding THCA is less about mystique and more about mindful selection.